Designed Janus Transition metal dichalcogenides Nanowall Electrodes with High Faradaic Efficiency for Nitrogen Reduction
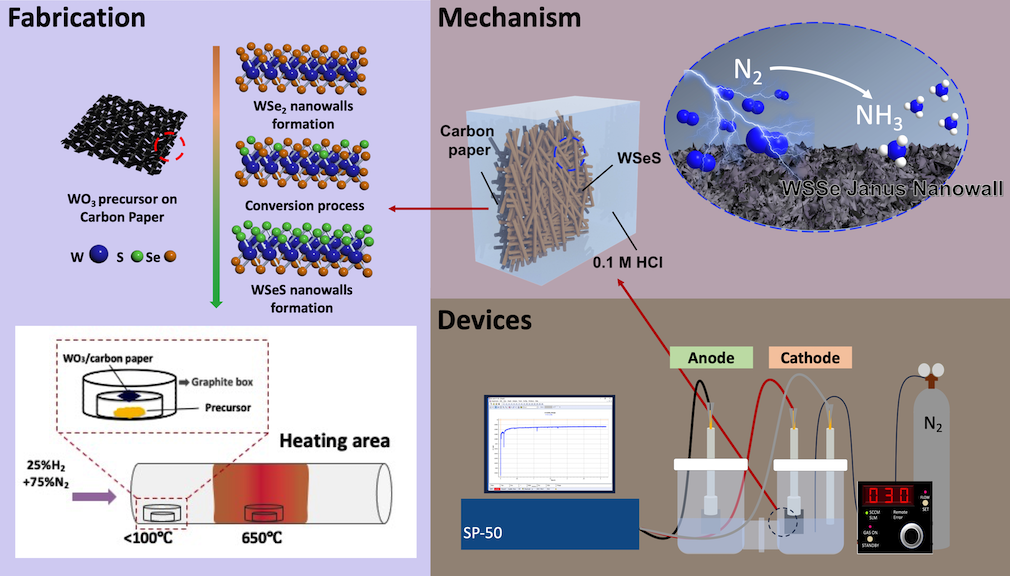


Ammonia is a critical feedstock in many everyday products and is conside
red a crucial energy carrier in the context of the energy transition. Despite
the fact that atmospheric nitrogen content is as high as 78 %, its high stab
ility and dissociation energy make the traditional Haber-Bosch (H-B) proc
ess require high energy consumption. In recent years, many studies have f
ocused on developing electrochemical nitrogen reduction (NRR) technolo
gy, which enables ammonia conversion under ambient conditions. Beside
s, many teams consider transition metal dichalcogenides (TMD) as crucial
materials for replacing precious metal catalysts due to their unique struct
ures, tunable bandgaps, and their applications in catalysis. Although TMD
s exhibit excellent catalytic properties, their active sites are limited to edg
es. Despite efforts to modify the surface through various techniques, the r
esults have often been unsatisfactory. However, in 2017, a Janus TMD was
successfully synthesized by artificially replacing sulfur atoms on one side
with selenium atoms. Janus TMDs have accelerated with the investigation
of out-of-plane asymmetric and intrinsic strain and electric fields, enablin
g the tuning of activity in TMD-based catalysts. This technique led to the s
uccessful synthesis of a 3D advanced semiconductor material, Janus WSe
S. It applies to emerging electrochemical NRR, achieving high selectivity a
nd Faradaic efficiency in ammonia conversion. Furthermore, the surface m
odification can be conducted using a plasma-assisted-seneizaion process,
for which JTMDs were successfully obtained. The preparation of electrode
s was confirmed through SEM, TEM, XPS, Raman spectroscopy, and so on.
The NRR behaviors were carried out using a potentiostat, resulting in the
production of ammonia. UV-Vis spectroscopy revea
National Tsing Hua University (NTHU), established in 1911 and located in Hsinchu, Taiwan, is one of the top research universities in the country. NTHU offers a wide range of programs in fields such as engineering, science, management, and humanities. The university is known for its strong emphasis on innovation, research excellence, and fostering global perspectives. With a commitment to academic rigor and interdisciplinary collaboration, NTHU plays a key role in advancing knowledge and technological development, contributing to both Taiwan’s growth and the global academic community.
.png)
Cost-Effective Anion Exchange Membrane Electrolysis for Green Hydrogen Production
Using innovative microbial technologies as a high-efficiencyvalued-added total solution for industriallivestock wastewater treatment
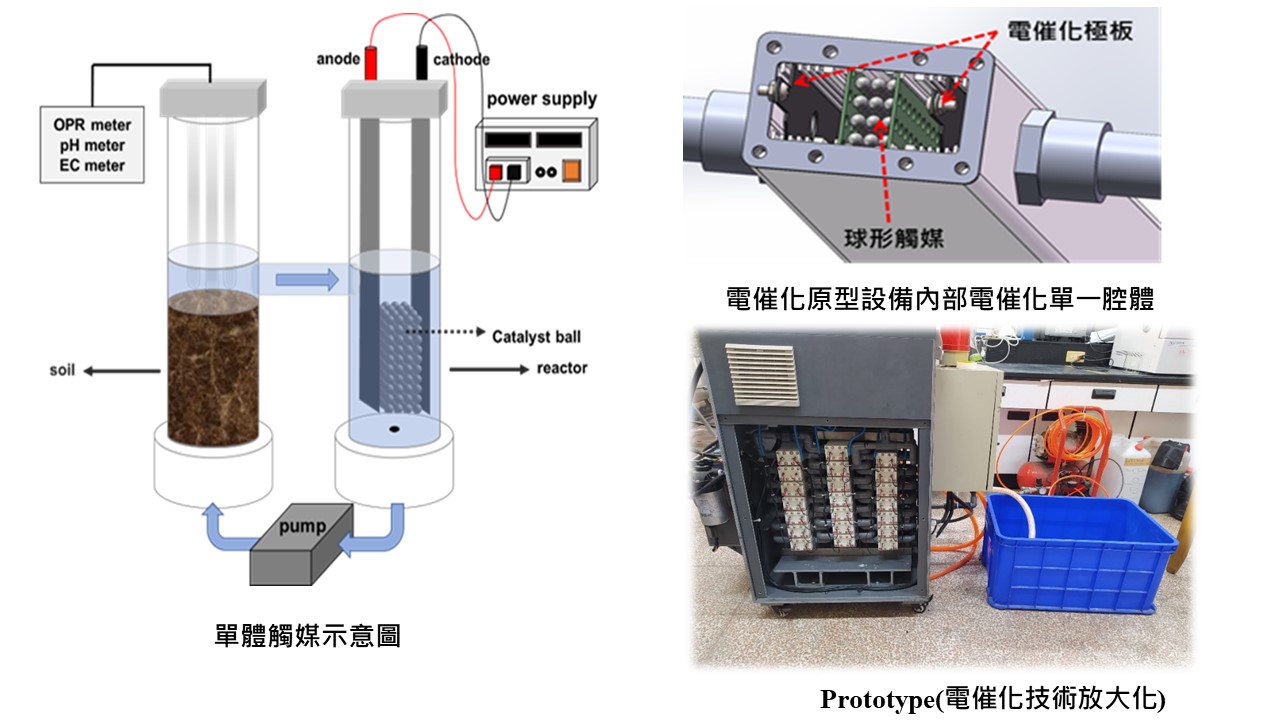
Application of innovative electrolyzed catalytic and nanobubble system for the remediation of petroleum-hydrocarbon contaminated soils and groundwater

High practicality surface modification technology for enhancing hydrogen production via water electrolysis and solid-state hydrogen storage efficiency
Technology maturity:Experiment stage
Exhibiting purpose:Display of scientific results
Trading preferences:Negotiate by self
Coming soon!