Porous Electrodes and Non-Precious Metal Catalysts: The Future of Anion Exchange Membrane Water Electrolysis Technology
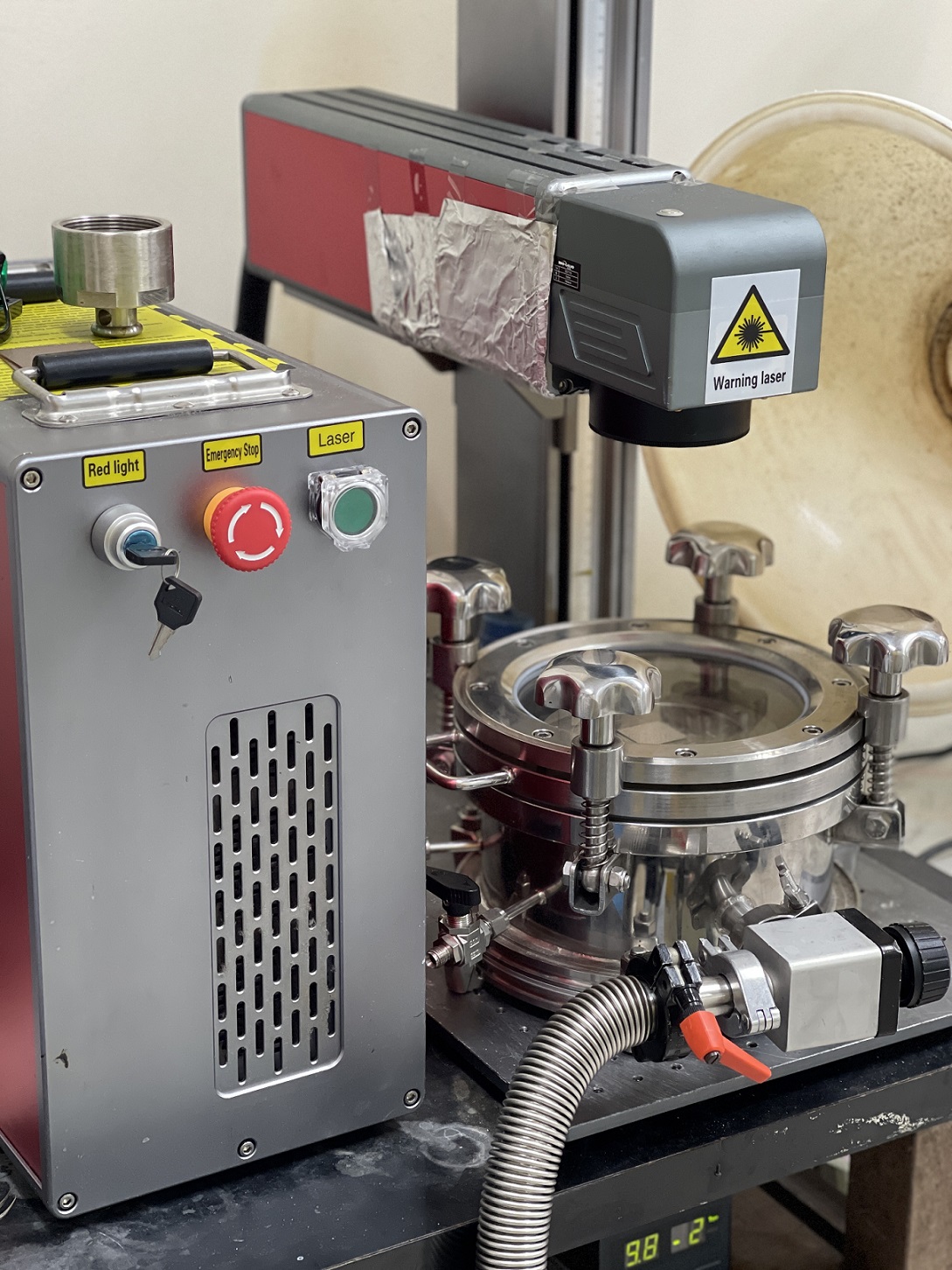
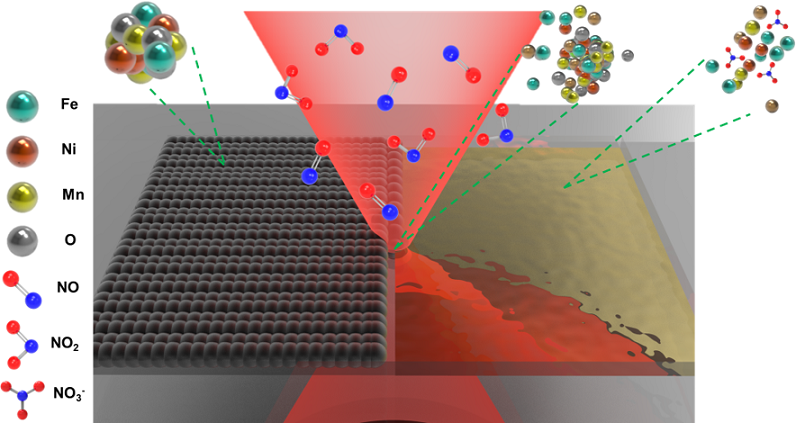

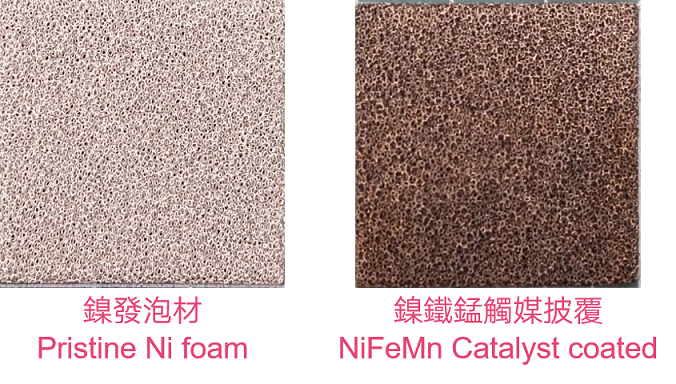



This technology utilizes the Pulsed Laser Irradiation Scanning on Mixed Salt Solutions method to develop a non-precious metal catalyst based on a Ni-Fe-Mn ternary alloy on metal porous materials, forming porous electrode structures. When applied to Anion Exchange Membrane Water Electrolyzers, it exhibits excellent performance. The technology is simple to operate, cost-effective, and fast to produce, enabling the rapid production of large-area, high-performance catalyst-coated porous electrodes.
National Central University is a public research university with long-standing traditions of the Republic of China based in Taiwan. It was founded in 1902 and renamed in 1915. The school was initially located in Miaoli when it first moved to Taiwan, but relocated to Zhongli in 1962 and developed into a comprehensive university. It's the first university in Taiwan to research industrial economics,[3] and economic development (Taiwan's Consumer Confidence Index is released monthly by NCU).[4] NCU is a member of AACSB.[5] NCU is one of the six national universities in research selected by the Ministry of Education.
Solid oxide electrolyzer integrated with ultra-low Pt catalysts proton exchange membrane fuel cells
.png)
Cost-Effective Anion Exchange Membrane Electrolysis for Green Hydrogen Production
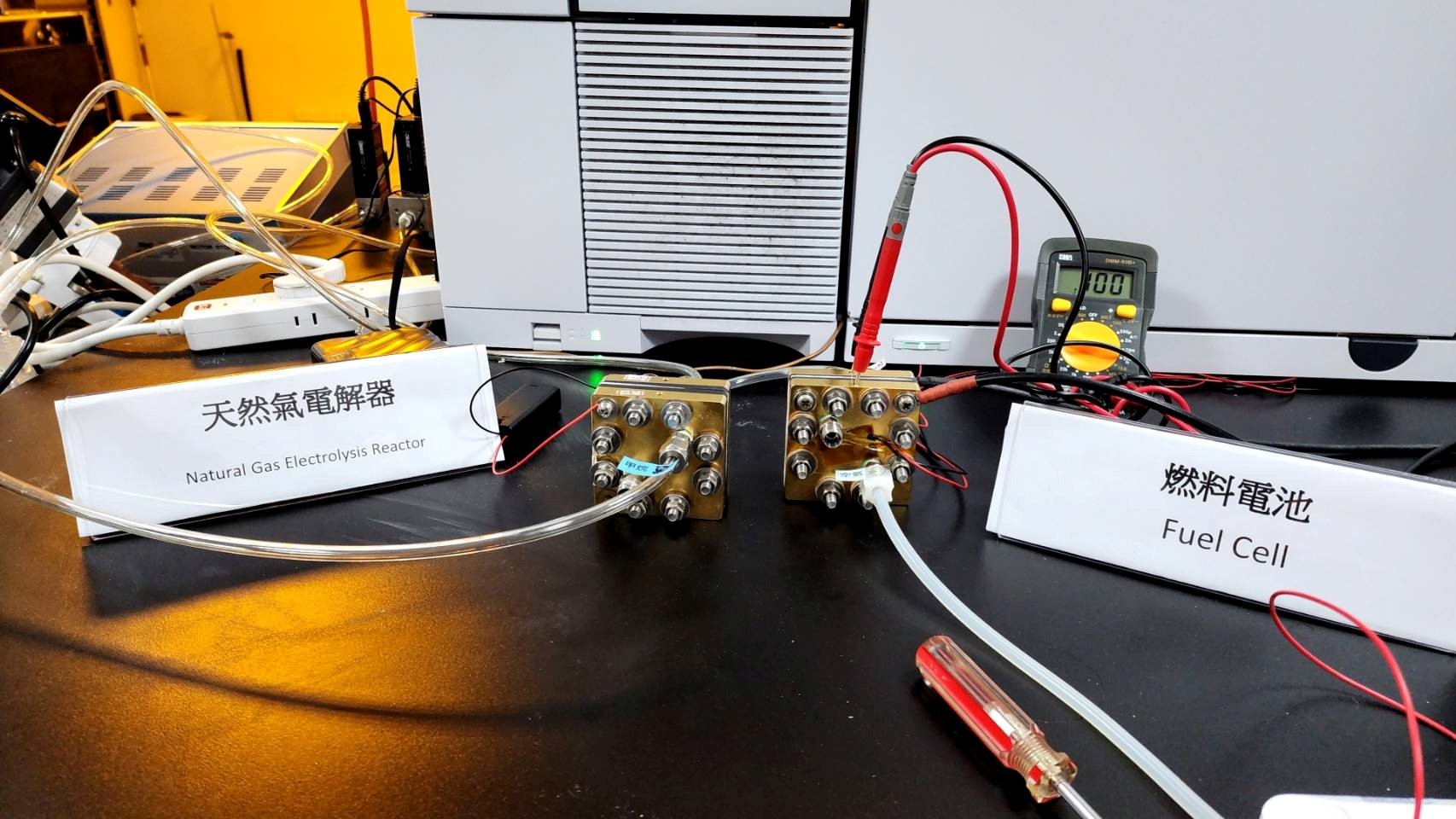
Non-precious metal catalysts driving advancements in natural gas electrolysis and fuel cell technologies

Generation of Low-Carbon Ozone and Negative-Hydrogen with Next-Generation Proton Exchange Membrane Water Electrolysis Technology
Technology maturity:Prototype
Exhibiting purpose:Display of scientific results
Trading preferences:Negotiate by self
*Organization
*Name
*Phone
*Main Purpose
*Discuss Further
*Job Category
*Overall Rating
*Favorite Area
*Key Tech Focus
*Willing to Receive Updates?
Other Suggestions
Coming soon!