Ammonia Production via Piezoelectric Nitrogen Reduction in Pure Water under Ambient Conditions
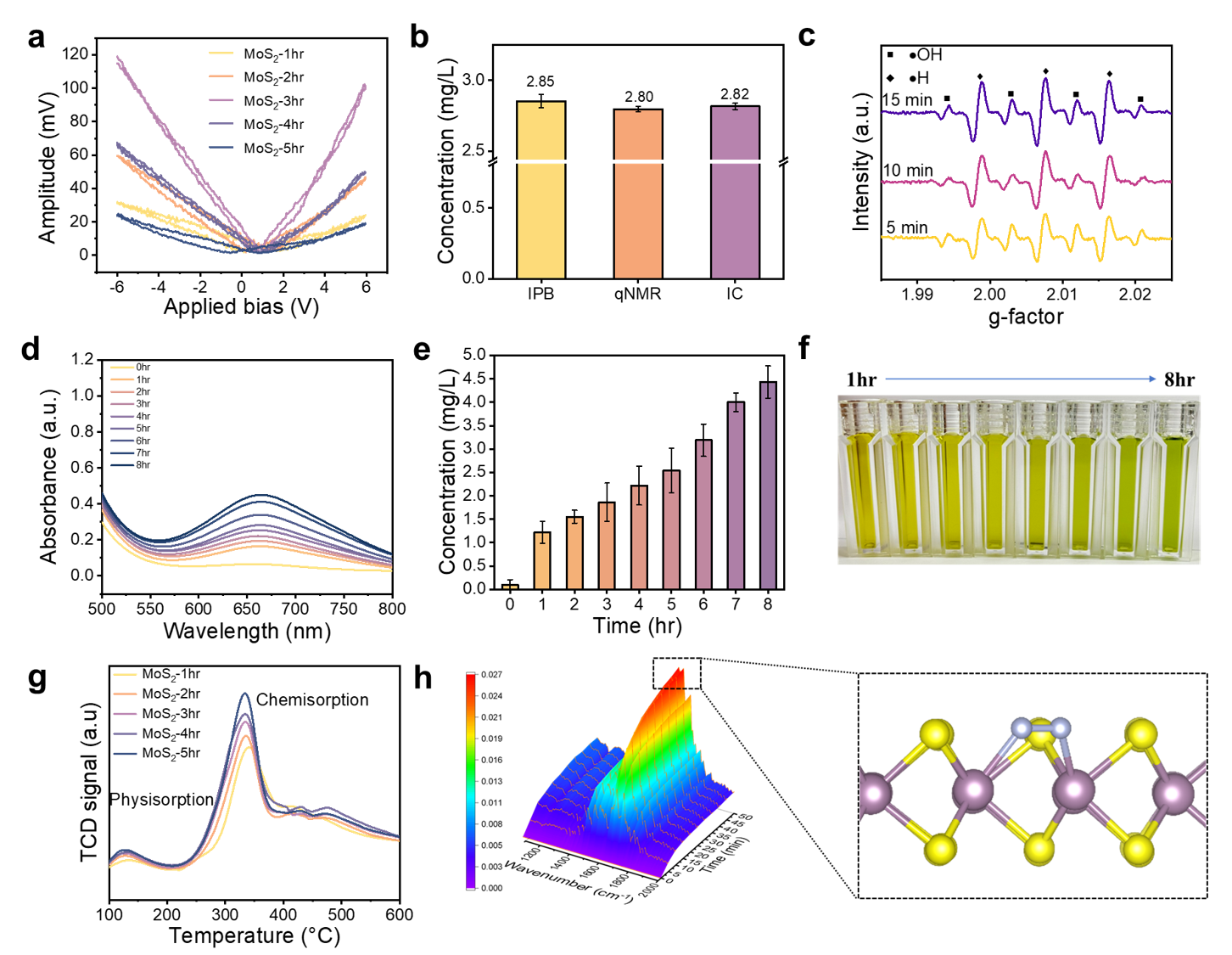
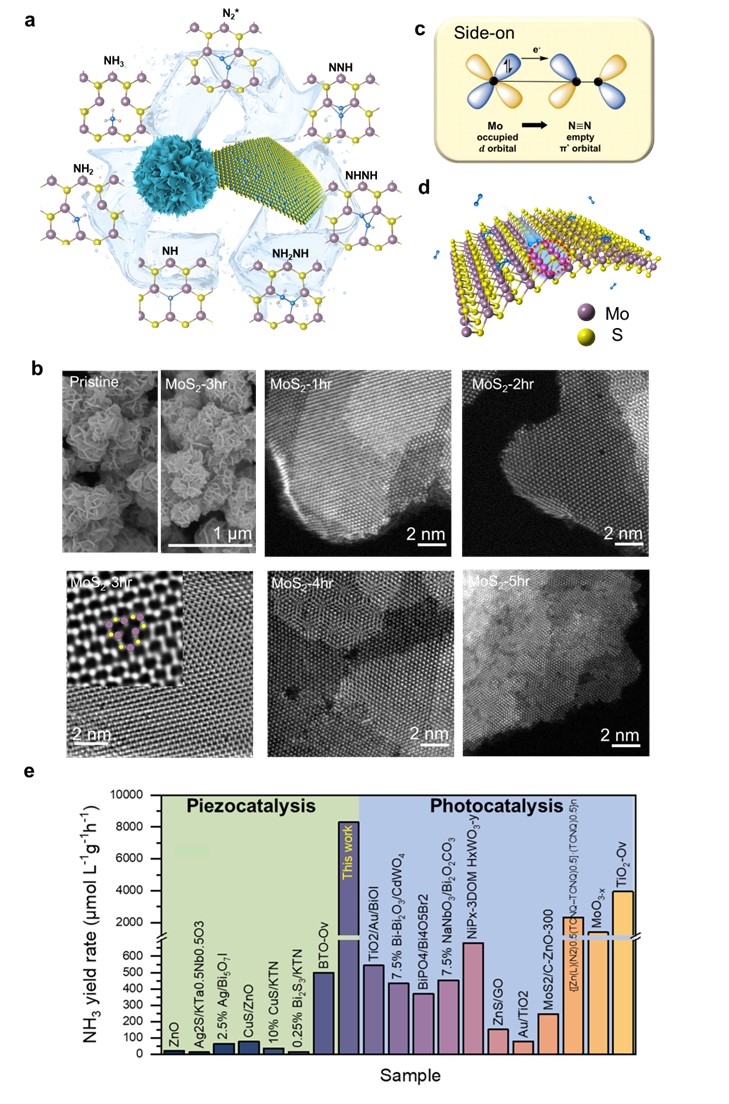
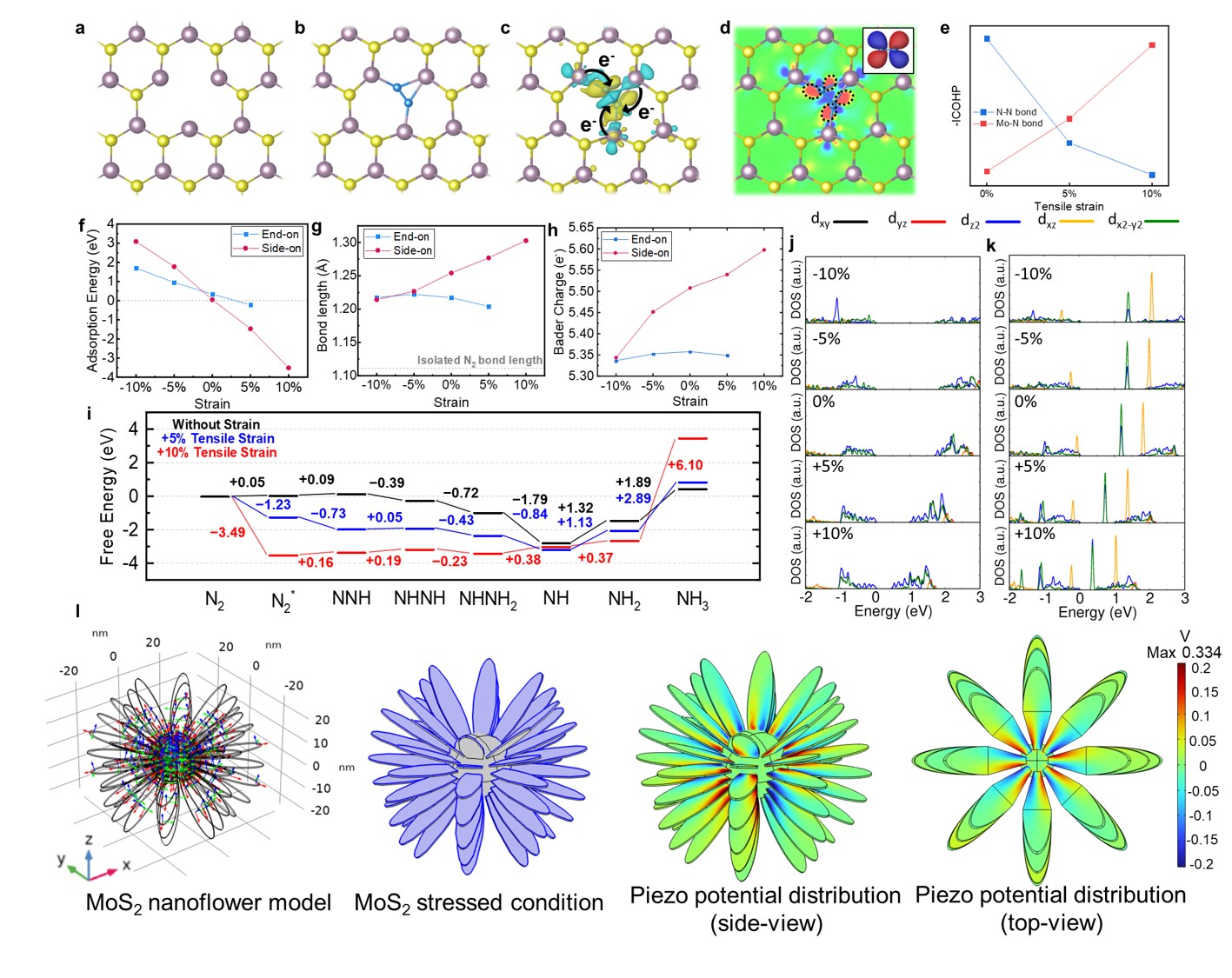



This study develops highly active MoS2 nanoflowers with sulfur vacancies as piezocatalysts. Utilizing mechanical energy, it reduces N2 to NH3 (8294.1 μmol L-1 g-1 h-1) in an atmospheric environmentwithout needing an external light source or electricity. The method enhances piezoelectric properties and nitrogen reduction, offering high selectivity similar to electro- and photocatalysis, without the complexity of electrode/electrolyte systems, providing a new green NH3 production alternative.
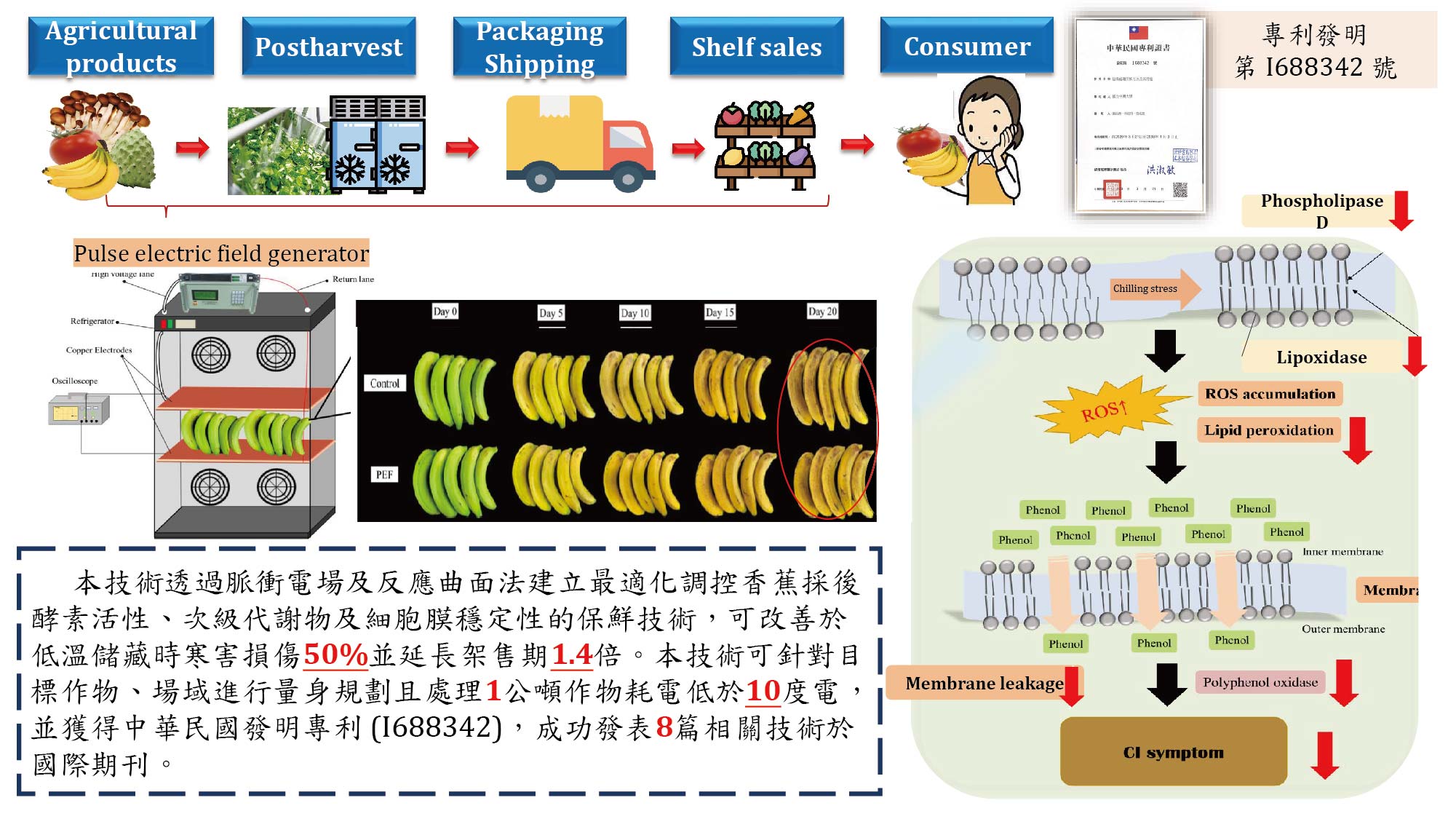
Application of a novel pulsed electric field technology to delay fruit chilling injury toward achieving a sustainable agricultural development goal
Inductively Heated Electrically Conductive Spacers to Enhance Membrane Distillation
Integrated Method for Improving Production Rate of Biogas Using Lignocellu-losic Depolymerization with Anaerobic Digestion

High practicality surface modification technology for enhancing hydrogen production via water electrolysis and solid-state hydrogen storage efficiency
Technology maturity:Prototype
Exhibiting purpose:Display of scientific results
Trading preferences:Negotiate by self
Coming soon!