
(1) Global Target of Carbon Neutrality by 2050: "Triple Carbon" Pressures
Driving Innovations
The World Bank reported that global carbon pricing revenue reached $53
billion in 2020. By 2030, carbon prices are projected to rise to $160 per to
n. The European Union proposed carbon tariffs, leading to changes in poli
cies, technology, and talent development worldwide.
(2) Steel Plants as Major Carbon Emitters: Decarbonization Focus on Blast
Furnace
The steel industry generates 3 billion tons of CO2 emissions annually, acco
unting for 9% of global emissions. Blast furnace ironmaking, responsible f
or 70% of these emissions, relies on energy and fossil-based reducing age
nts, resulting in significant CO2 emissions. Decarbonizing blast furnaces is
crucial for achieving net-zero emissions.
(3) Essential Pathway for Steel Plants: "Hydrogen-rich Blast Furnace"
Using hydrogen as a fuel and reducing agent in iron smelting, hydrogen
metallurgy reduces CO2 emissions. The "hydrogen-rich blast furnace" is a
leading technology for green and low-carbon steel production.
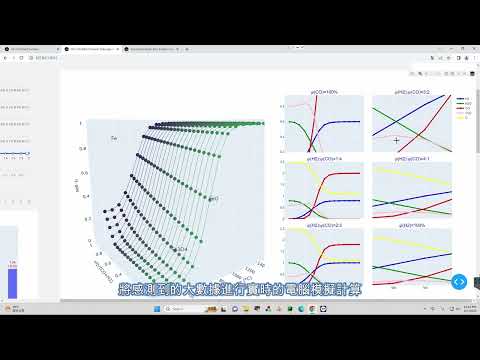
(4) Opening the "Black Box of Blast Furnaces": Hydrogen-rich Blast Furnac
e Digital Twin System
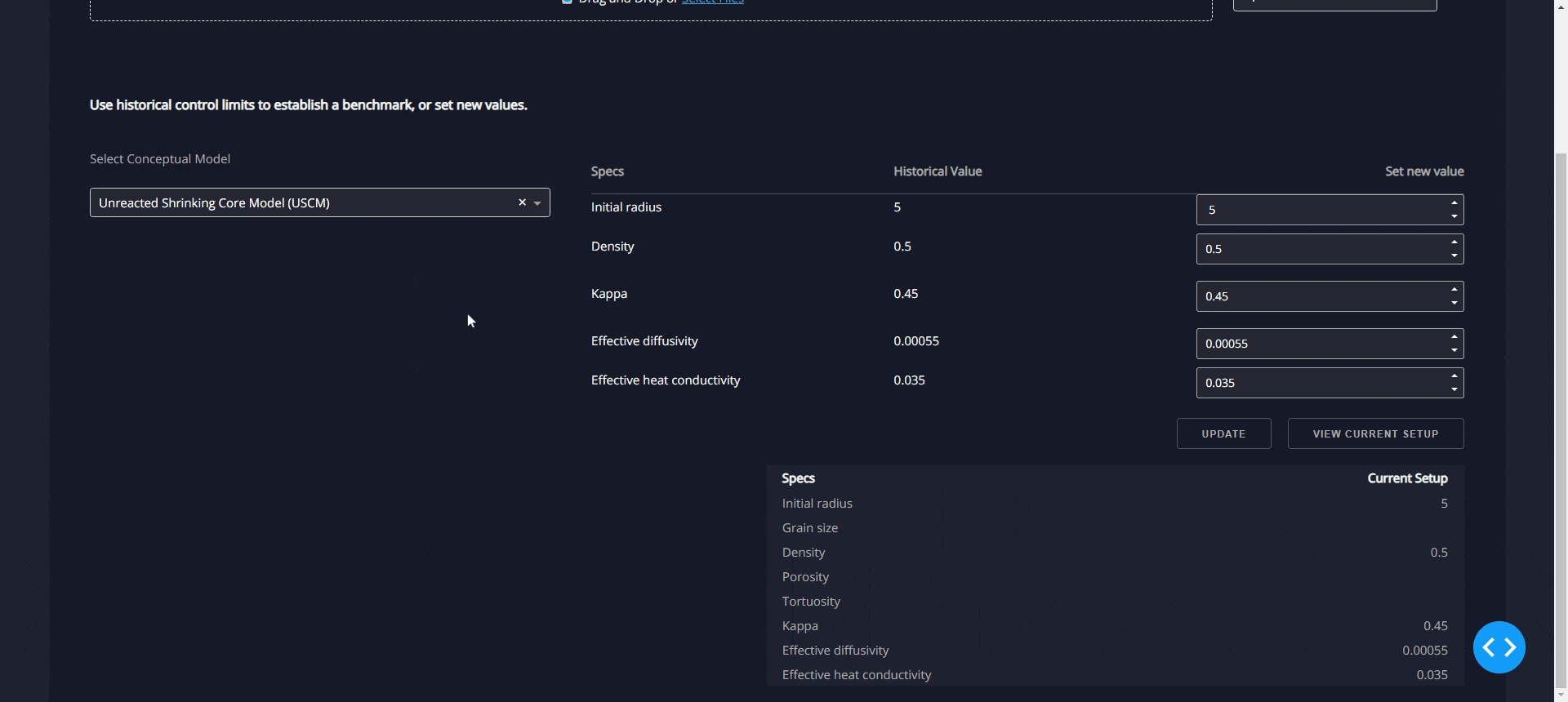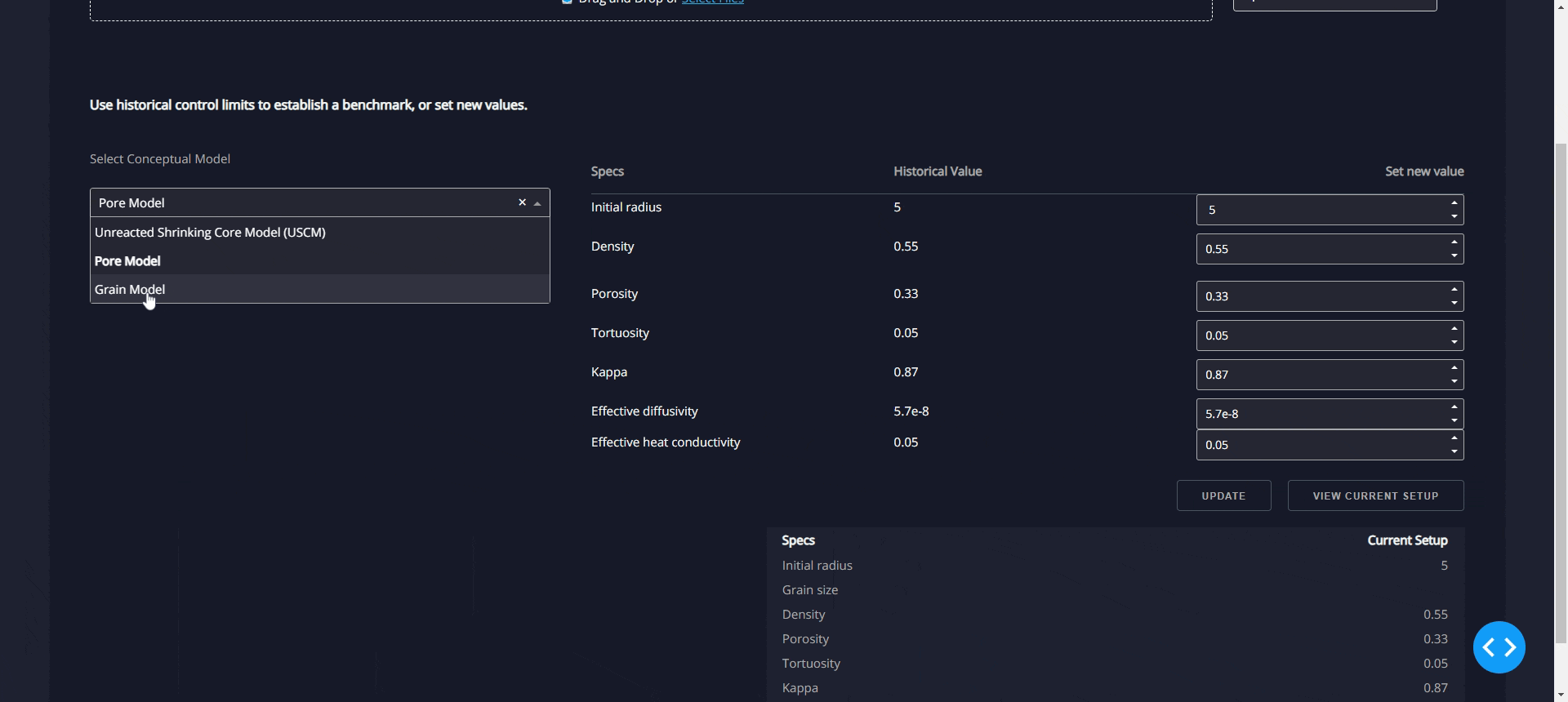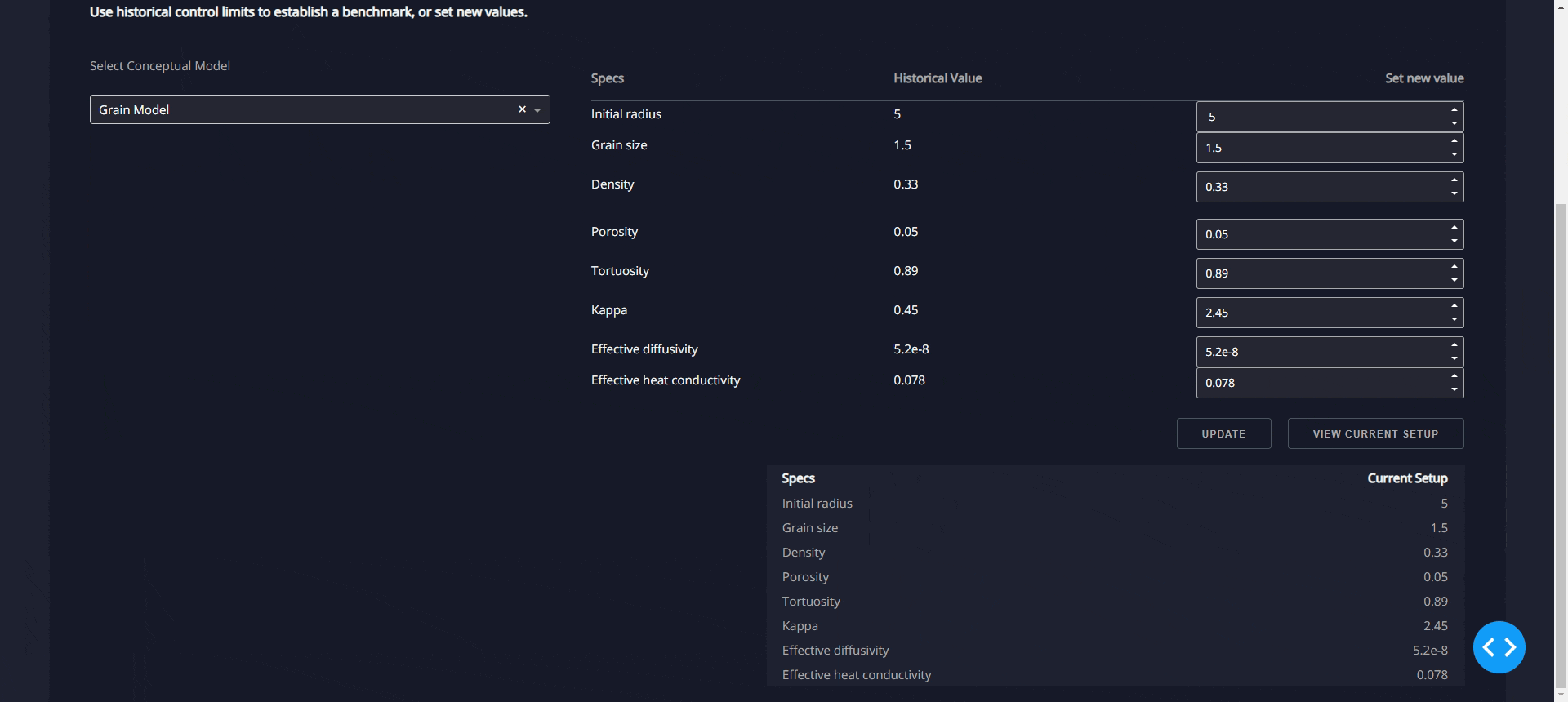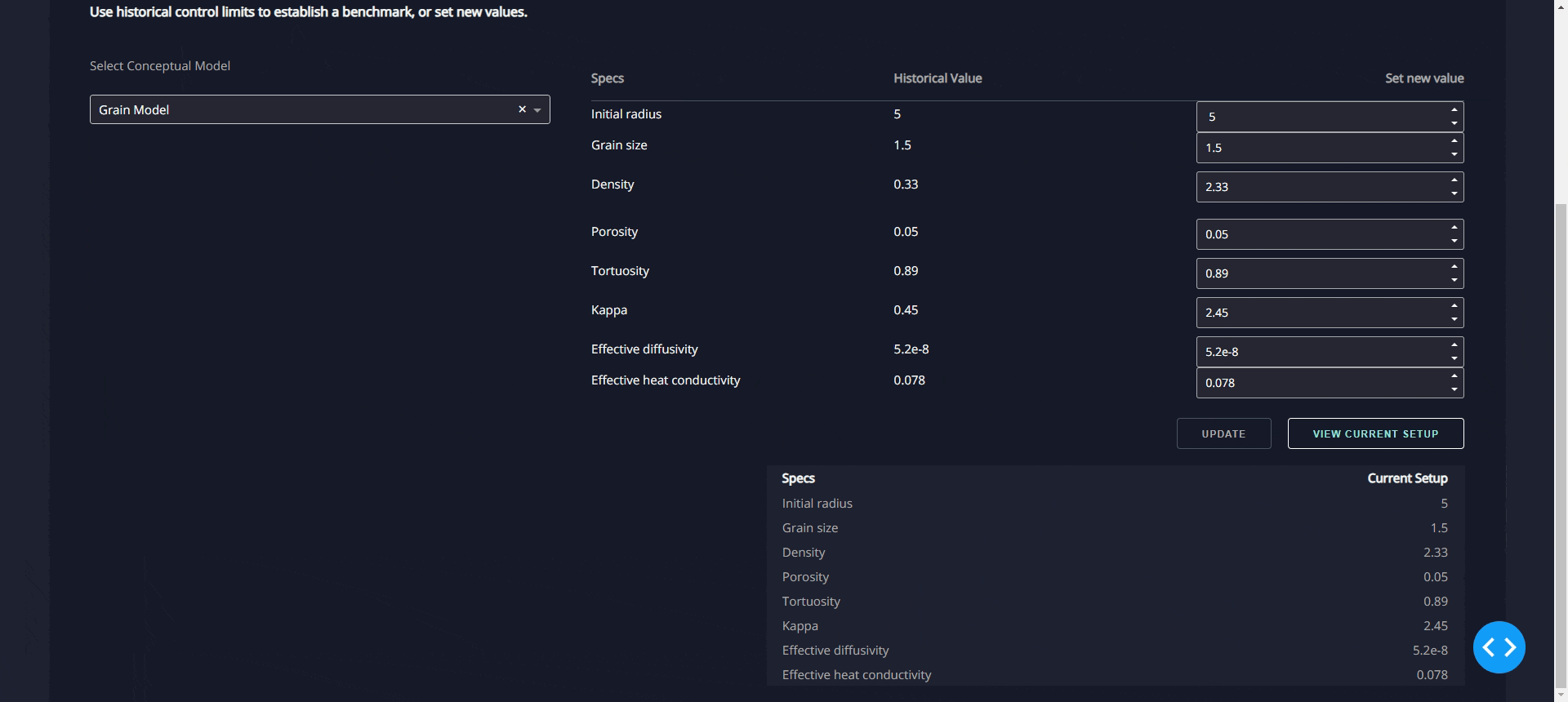
(a)"Blast Furnace Thermodynamic Calculation Software" can calculate the
thermodynamic equilibrium conditions of various furnace locations in real
-time based on the data obtained from blast furnace monitoring. By iterat
ively solving the complex thermodynamic equilibrium relationship betwee
n gas concentration, temperature, and pressure, it translates the thermod
ynamic conditions into "real blast furnace operating conditions," which is
the key technology to open the blast furnace black box; (b) "Visualized Re
duction Kinetics Model" takes the obtained "real blast furnace operating c
onditions" as input and utilizes reaction kinetics models to predict the co
mplex reaction behavior of iron ore within the blast furnace, achieving hy
drogen-enriched blast furnace digital twinning technology with real-time
predictive capabi
Due to NCKU’s rapid development, the R&D Committee has become increasingly important. In order to meet the needs of NCKU's academic research planning, integration, industry cooperation and academic cooperation, it has become an independent operating unit for practical functions. Therefore, in the 5th University Council of the 1994 academic year, the R&D Committee was renamed the Office Of R&D(ORD) after the amendment of Article 8 of NCKU’s organizational regulations. NCKU Regulations Governing the Establishment of the Office of Research and Development were approved in the 7th University Council of the same academic year. In addition to the original three divisions, the instrumentation equipment center was established for integration and planning of NCKU’s relevant instrumentation and equipment, bringing further into play the overall function of ORD, which will be more beneficial to NCKU’s teachers and students. In June 2006, the Office of International Academic was established. The Academic Cooperation Division of ORD Department was converted into the International Cooperation Division and shifted to the Office of International Academic. Original URL: History and Vision https://en.ord.ncku.edu.tw/article-history.html The copyright belongs to the author. For commercial reprints, please contact the author for authorization, and for non-commercial reprints, please indicate the source.
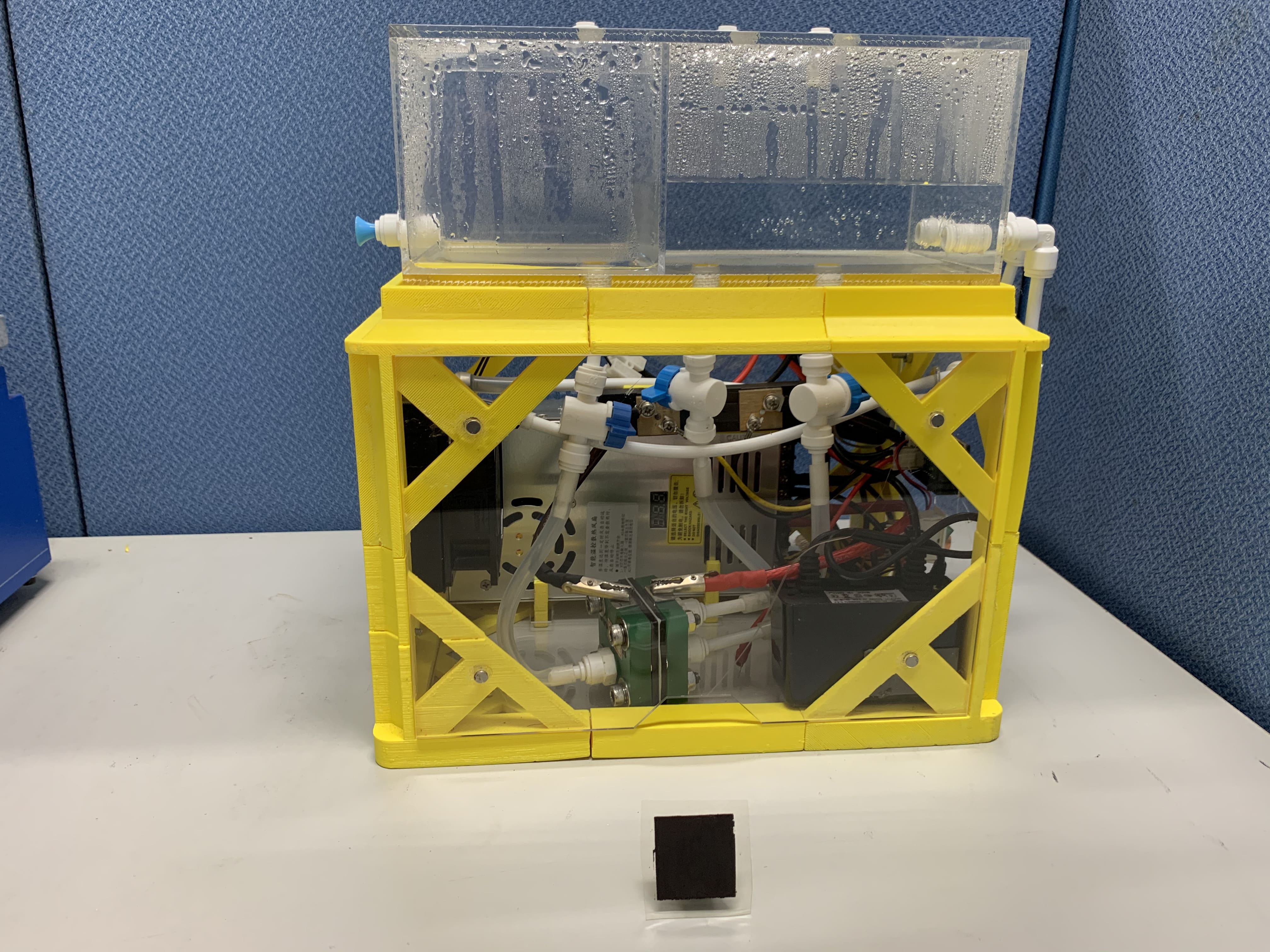
Renewable hydrogen economy- R&D of electrolysis energy storage and application of green hydrogen industry-academia consortium project

Green adsorption materials and energy-saving exhaust gas treatment equipment used in the treatment of industrial volatile organic compounds
Solvent recycling (solvent collection) system; CLEAN-ACE800 series Continuous Vacuum Distillation Recovery System
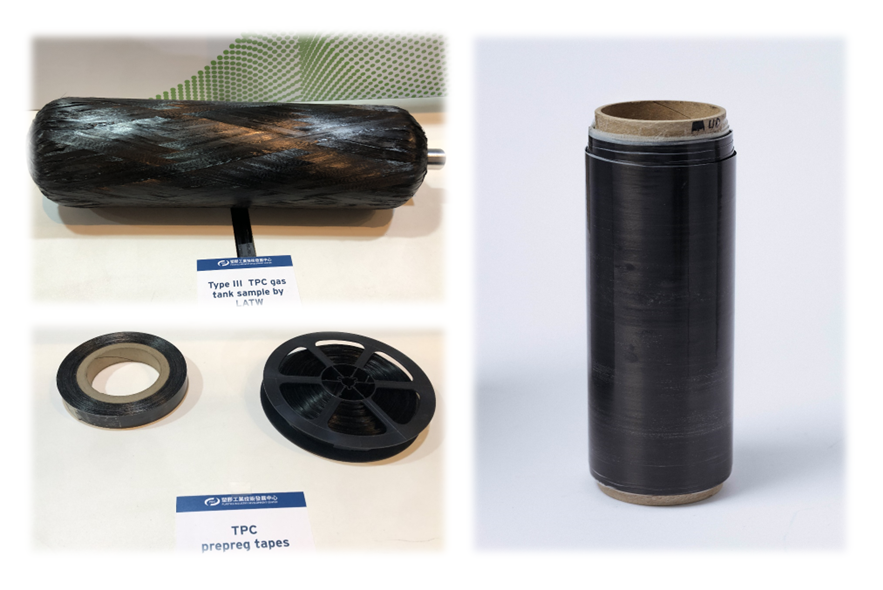

Development of a New Generation of Hydrogen Storage Tanks - Ultra-Thin Thermoplastic Winding Tape Process Technology
Technology maturity:Experiment stage
Exhibiting purpose:Display of scientific results
Trading preferences:Negotiate by self
Coming soon!